In the ever-evolving landscape of enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, Oracle E-Business Suite (EBS) has stood the test of time as a premier solution for managing financial processes. As the sun sets on traditional on-premises database management systems (DBMS), a new dawn emerges in the realm of cloud-based solutions. As an Oracle architect with two decades of experience in EBS Financials, we embark on a voyage to explore the uncharted waters of cloud DBMS innovation. In this article, we’ll delve into the winds of change, the currents of scalability, and the constellations of security that guide us toward a brighter future. Cloud computing has revolutionized the way organizations approach IT infrastructure, offering scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness previously unimaginable with traditional on-premises solutions.
The Winds of Change
In the context of EBS Financials, the transition to Cloud DBMS represents a natural progression towards modernization and agility. By migrating critical financial data to the cloud, organizations can leverage the power of distributed computing to optimize performance, reduce latency, and ensure high availability. Furthermore, Cloud DBMS eliminates the need for costly hardware investments and maintenance, empowering businesses to allocate resources more efficiently.
Serverless Architectures
Imagine a world where you don’t worry about provisioning servers, scaling, or patching. Serverless DBMS services, such as Amazon Aurora Serverless, Azure SQL Database Serverless, and Google Cloud Firestore, allow developers to focus solely on their applications. These systems automatically adjust resources based on demand, like a ship adjusting its sails to catch the wind.
Below depicts one of the popular serverless architectures:
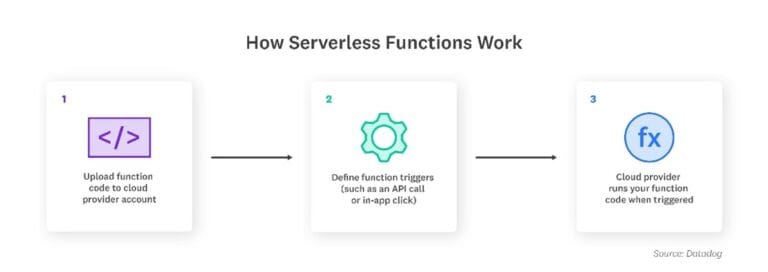
Function as a Service (FaaS), a popular type of serverless architecture, allows developers to focus on writing application code. Amazon introduced the first mainstream FaaS platform, AWS Lambda, in 2014. Currently, a majority of developers still use AWS Lambda to build serverless applications, but Google and Microsoft have their own FaaS offerings as well, called Google Cloud Functions (GCF) and Azure Functions respectively.
Multi Model Database
The cloud encourages diversity. Multi-model databases, like Amazon Neptune and ArangoDB, support various data models (graph, document, key-value) within a single platform. Just as a skilled sailor adapts to changing tides, these databases adapt to different use cases seamlessly.
The Currents of Scalability
- Elastic Scaling: In the cloud, scalability is not a distant island—it’s a built-in feature. Elastic scaling allows DBMS to expand or contract resources dynamically. Whether you’re handling a gentle stream of data or a roaring waterfall, your database adjusts accordingly
- Global Distribution: Like ocean currents connecting distant shores, global distribution ensures data availability across regions. Services like Azure Cosmos DB and Google Cloud Spanner replicate data worldwide, providing low-latency access to users everywhere.
The Constellations of Security
- Encryption at Rest and in Transit: Just as ancient mariners navigated by the stars, modern cloud DBMS rely on encryption. Data at rest and in transit must be protected. Services like AWS RDS and Microsoft Azure encrypt data using industry-standard algorithms.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): IAM acts as our celestial compass. Fine-grained access controls ensure that only authorized crew members can access the data. Azure AD and Google Cloud IAM steer the ship toward secure waters.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the invention of Cloud DBMS represents a paradigm shift in database management, offering unparalleled opportunities for innovation and efficiency in EBS Financials. As Cloud DBMS continues to evolve, so too will its impact on EBS Financials and the broader ERP landscape. Looking ahead, advancements in areas such as edge computing, blockchain technology, and quantum computing hold the promise of further enhancing the capabilities of Cloud DBMS and unlocking new opportunities for innovation. We see a future where cloud DBMS sail confidently through storms and calms alike. The Oracle of old meets the nimble winds of innovation, and together, we chart a course toward a data-driven world.





